- Latin Name: Symplocarpus foetidus
- Appearance: The flowering part of this plant emerges before the leaves. The tiny petalless white flowers are on a club-shaped spadix, which is covered with a deep purple spotted hood known as a spathe. After the flower, leaves burst into large cabbage-like foliage. You may smell this plant before you see it because skunk cabbage emits a foul, skunky odor to attract pollinators such as flies, gnats, and beetles.
- When: February - April
- Locally found: Rock Cut State Park, Severson Dells
- Habitat: wet, marshy habitats.
- Fun Fact: Skunk cabbage is usually one of the first plants to sprout in early spring, even through ice and snow! This is because the flower carrying spadix produces heat that can melt the surrounding area for its emergence.
FIELD NOTES BLOG
Spring Wildflower Spotting
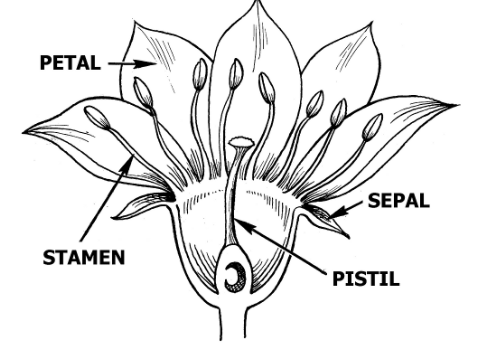
There are so many signs of spring around us this time of year. The world feels like it is waking up again when you feel the sun on your face, spot birds flying north, and perhaps see the prettiest sign: wildflowers. Between our prairie, forest, and aquatic habitats at Severson Dells and beyond, there will be countless wildflower blooms to discover within a few weeks. To point out these fantastic flowers by name, you will need to know some identifying features. To help you on this quest, you can start by familiarizing yourself with some of the fundamental components of flowers in the diagram below. Once you are a flower anatomical expert, you can read about some of our local wildflowers and how each one is uniquely beautiful!
Skunk Cabbage
White Trout Lily
Wild Ginger
Sharp-lobed Hepatica
Bloodroot
Dutchman's Breeches
Virginia Waterleaf
Prairie Trillium
Virginia Bluebells
Common Blue Violet
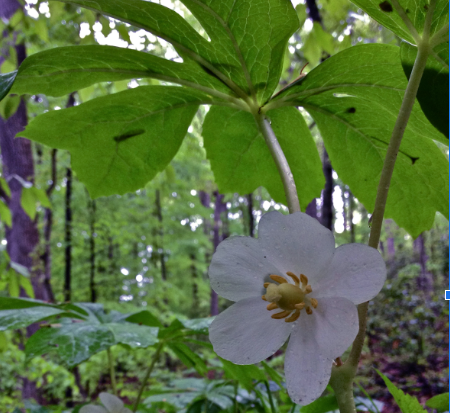
Mayapple
Cut-Leaved Toothwort
Pasque Flower
New Paragraph
Sources
Ohio Department of Natural Resources - Skunk Cabbage
University of Texas Wildflower Center - White Trout Lily
U.S. Forest Service - Wild Ginger
Grow native Missouri Prairie Foundation - Sharp-lobed Hepatica
Britannica - Bloodroot
U.S. Forest Service - Dutchman’s Breeches
Wisconsin Horticurture - Virginia Waterleaf
The Moron Arboretum - Prairie Trillium
Cornell Botanic Gardens - Virginia Bluebells
NC State Extension - Viola Sororia
Cornell Botanic Gardens - Mayapple
U.S. Forest Service - Cut-leaved Toothwort
Montana Field Guide - Pasqueflower
iNaturalist - Observations Map

RECENT ARTICLES






































