FIELD NOTES BLOG
The Importance of Spiders
While most people are scared of spiders, spiders are more afraid of humans. People will claim that spiders are scary and will bite you, but the truth is, they’re helping you more than they’re doing any harm. Spiders play a very crucial role in the food chain: they are the link between other insects, such as flies and mosquitos, to small mammals, such as birds and amphibians. This means that spiders are both prey and predator, so they are an essential part of the food chain. Although spiders tend to be forgotten about when discussing the ecosystem, they still are of great importance to humans.

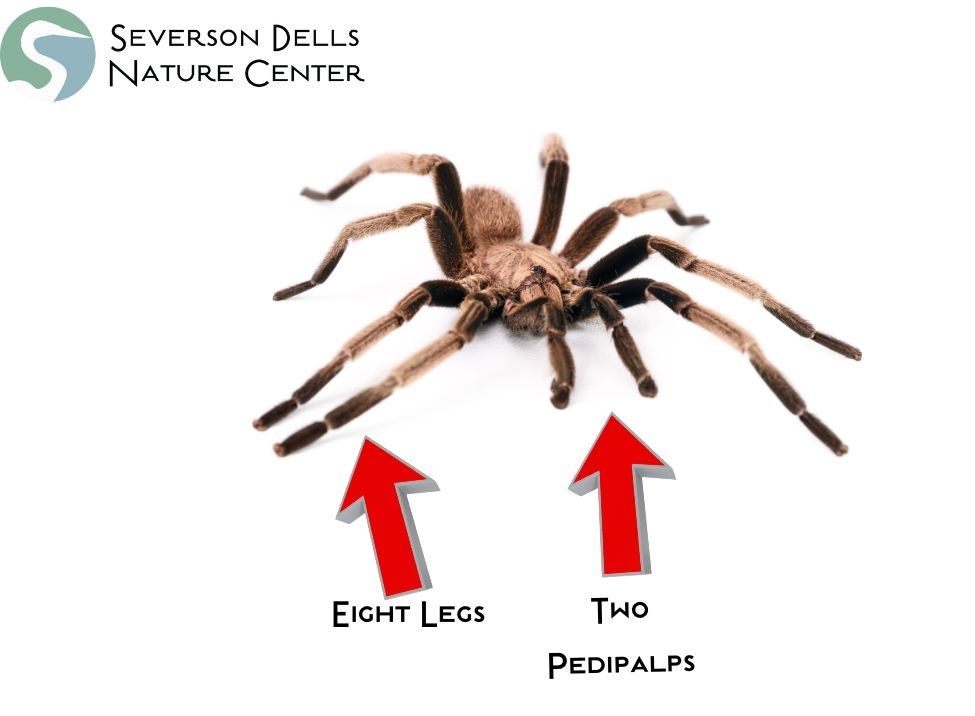
Spiders are small, light creatures, and they are incredible hunters. Most spiders have eight eyes, which allows them to have a keen sense of motion in almost 360 degrees. However, spiders rely on their other senses more than their vision, primarily touch, smell, and taste. Spiders have an extensive array of sensory organs and appendages situated throughout their pedipalps (the second set of appendages located next to their mouth) and their legs.
Pedipalps are flexible joints that are covered with short hairs, these are sensory hairs and they allow spiders to touch and taste things. Their bodies are covered in tiny hairs and slits, which can sense vibration as well as the direction the vibration is coming from. These hairs and slits are extremely sensitive, to the point that spiders can identify what type of insect is on their web just from the different vibration patterns. Spiders are considered
generalist predators, meaning they eat a wide variety of prey, not just certain species. A spider's diet primarily consists of insects, making them extremely helpful creatures when it comes to pest elimination and population control; many people consider having a spider in their garden to be useful because it stops annoying pests from eating their plants.
Spiders are unique and beneficial creatures because of their silk production. Spiders make their webs out of silk, which is a useful material due to its strength properties. Silk is extremely flexible and can withstand high stresses, making it a very useful textile material for clothing, ropes, nets, bandages, and so much more. While humans have many uses for silk, the spider's use of it is by far the most interesting. Spiders produce silk and then weave it into a web, which the spider then uses as its habitat. Webs do more than just protect spiders from the elements, they also act as a catch-and-trap system for other resources such as food and water. Spiders use their weaving skills and the durability of their web to trap and entangle their prey, making it almost impossible for them to release and ultimately suffocating them to death. Silk has a high porosity, meaning spider webs can collect water droplets as they fall from the sky or neighboring plants. Silk can shift its fiber structure in the presence of humidity, allowing the falling raindrops to adhere to it, and travel along the smooth strands of the web; where it will bubble and stay until the spiders decide to collect and drink it. Spider webs are great bioindicators of air pollution and heavy metal seepage because of the silks' highly absorptive properties.

Silk isn’t the only useful material that comes from spiders. Spiders also produce a very intriguing kind of venom, which can be used for more than just a defense mechanism. Spider venom contains proteins and polypeptides, meaning it can modulate channel ions, which is very helpful in the medical field, as these peptides have proven to provide antimicrobial and neuroprotective effects for humans. Studies from the National Library of Medicine have proved that biotoxins have antitumor potential; when peptides are separated from the venom they can “impair tumor cell membrane, inhibit cancer cell growth, or induce apoptosis”. This is extremely beneficial when it comes to treating cancerous tumors, cells, and chronic pain. Spider venom has been used in pharmaceutical production for many years; due to its potency, accurate target detection, and fast-acting capabilities. The venom is already an active ingredient in some medications used for strokes, cancer, pain, erectile dysfunction, epilepsy, and high blood pressure. As more research is done, we may discover that spider venom might have more benefits and uses than we currently know about.
Now that you’re aware of how important and helpful spiders are to humans and the environment, the next time you see a spider in your house, think of moving it outside instead of killing it. Think of all the benefits the spider could provide for you or a loved one as you’re relocating it. Remind yourself how spiders are equipped with unique venom and silk, how much they can tell us about the health and management of the environment they live in, and how helpful they are to humans. Spiders are essential creatures, so let's treat them like they are and give them the respect they deserve!
Sources:
Smithsonian Office of Educational Technology. “Smithsonian Learning Lab Collection: Smithsonian in Your Classroom: "Under the Spell of ...Spiders!".” Smithsonian Learning Lab, Smithsonian Office of Educational Technology, 20 Jul. 2016, https://learninglab.si.edu/q/ll-c/RbTjJfyet3B6ru3d
Admin. “The Many Benefits of Spiders.” Southern Pest Control, 18 Oct. 2022, www.southernpestcontrol.com/the-many-benefits-of-spiders/#:~:text=They%20are%20important%20not%20only,enriches%20it%20with%20vital%20nutrients.
Laviopierre, Frederique. “Garden Allies: Wandering and Hunting Spiders.” Pacific Horticulture, 10 May 2024, pacifichorticulture.org/articles/wandering-and-hunting-spiders/.
Wu, Ting, et al. “Spider Venom Peptides as Potential Drug Candidates Due to Their Anticancer and Antinociceptive Activities.” The Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins Including Tropical Diseases, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 3 June 2019, pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6551028/.

RECENT ARTICLES